This mode is used to create a new 3D volume composed of parallel slices from one or more source group of slices.
The source slices do not have to form a 3D group. They can be in any orientation. You can have missing slices in the source group. Your source dataset can even be a spherical system.
The re-sliced volume will always be in a Cartesian system, with the slices in either Axial direction (X-Y plane), Coronal direction (X-Z plane), Sagittal direction (Y-Z plane) or Oblique. All the slices will be equidistant.
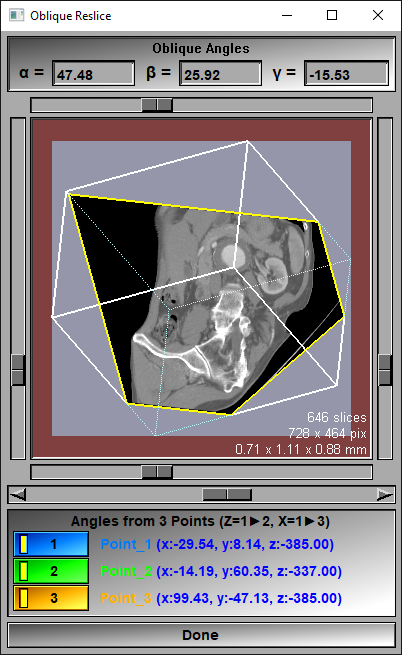
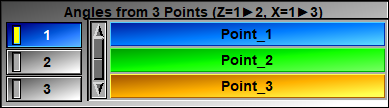
When reslicing in an Oblique plane, you can specify the plane orientations by either 3 angles values, or a new axis system aligned with 3 points.
•When using 3 points, the first 2 points define the new "Z" axis, while the first and third points define the new "X" axis.
•When using 3 angles, we start from an axial system, a first rotation Alpha (α) is performed around the "X" axis of this system, a second rotation, Beta (β), is performed around the "Y" axis of the transformed system and finaly, a third rotation, Gamma (γ), is performed around the the "Z" axis of the transformed system.
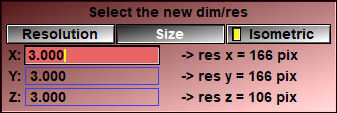
If desired you can have isotropic voxels (the voxel spacing equal in the 3 (X/Y/Z) directions).
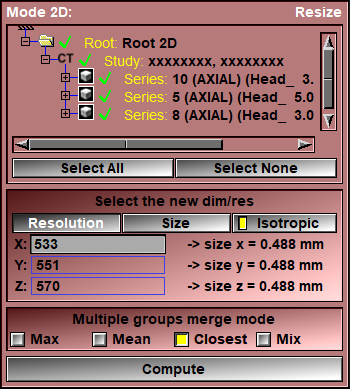
If you select multiple groups of images as the source, the resulting volume will cover the complete volume of the sources.
By default the suggested resolution and pixel size are computed to insure a one to one match between the original and reslice volumes.
Since the re-sliced volume will cover the entire volume of the source groups, by specifying a new resolution, the voxel's size are automatically re-computed and vice-versa.
If you select multiple source groups and they overlap, the resulting re-sliced voxels in the overlapped regions will be a merge of the sources voxels. You have a choice of 4 merge techniques:
•Max: The maximum value of all the overlapping voxels is used.
•Mean: The mean value of all the overlapping voxels is used.
•Closest: We compute the distance between the center of the re-slice voxel and the nearest center of the source voxel for each groups. We keep only the value from the closets voxel.
•Mix: The weighted value of the 3 closest voxels. We sum the voxel values, starting with the closest, each successive voxels having half the weight of the previous ones.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
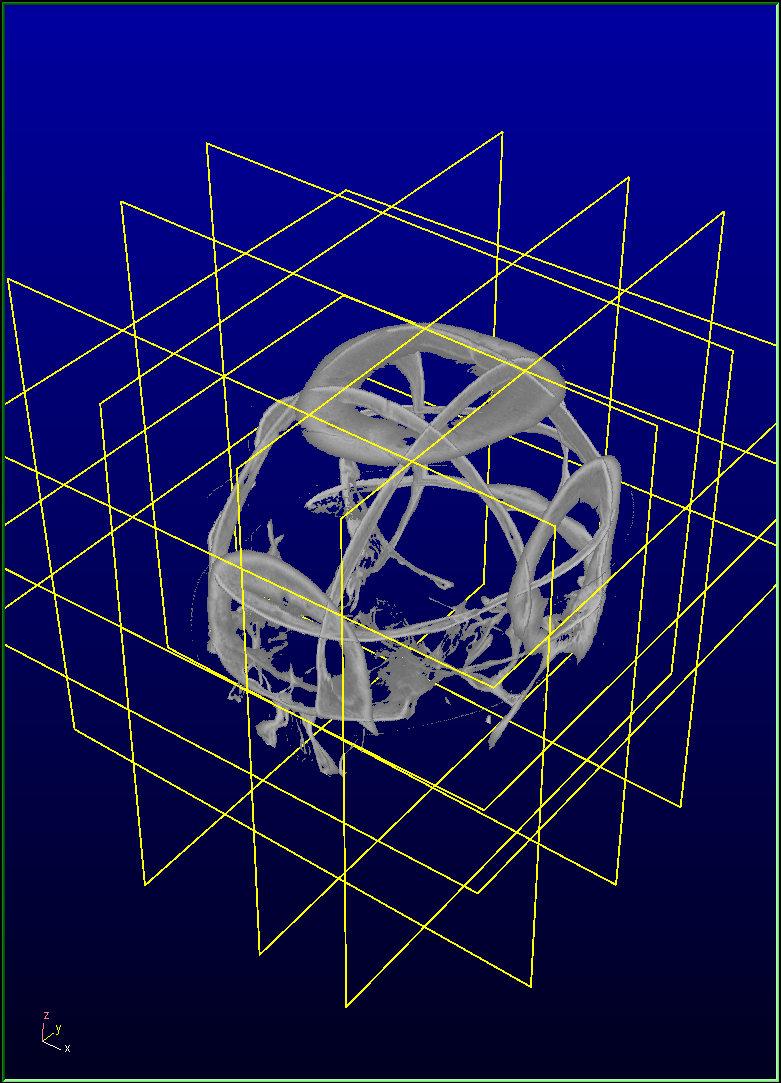
3 dataset in 3 directions
|
Reslice axial dataset |
Reslice coronal dataset |
Reslice saggital dataset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
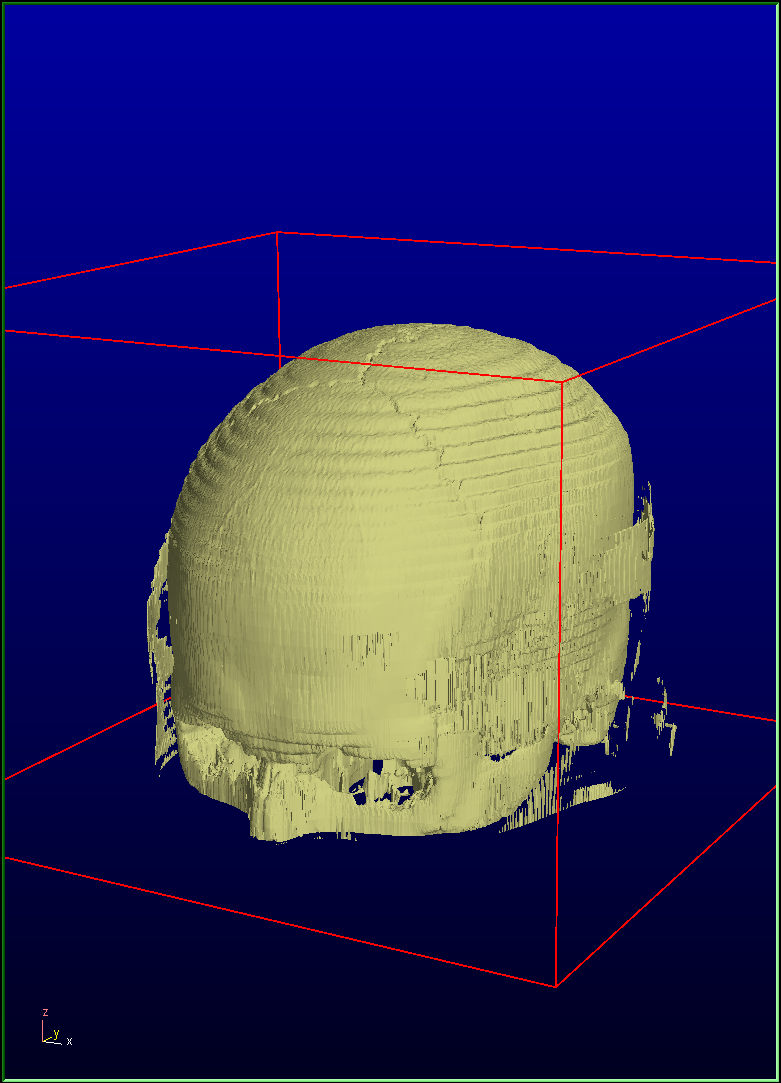
Reslice all datasets: Max |
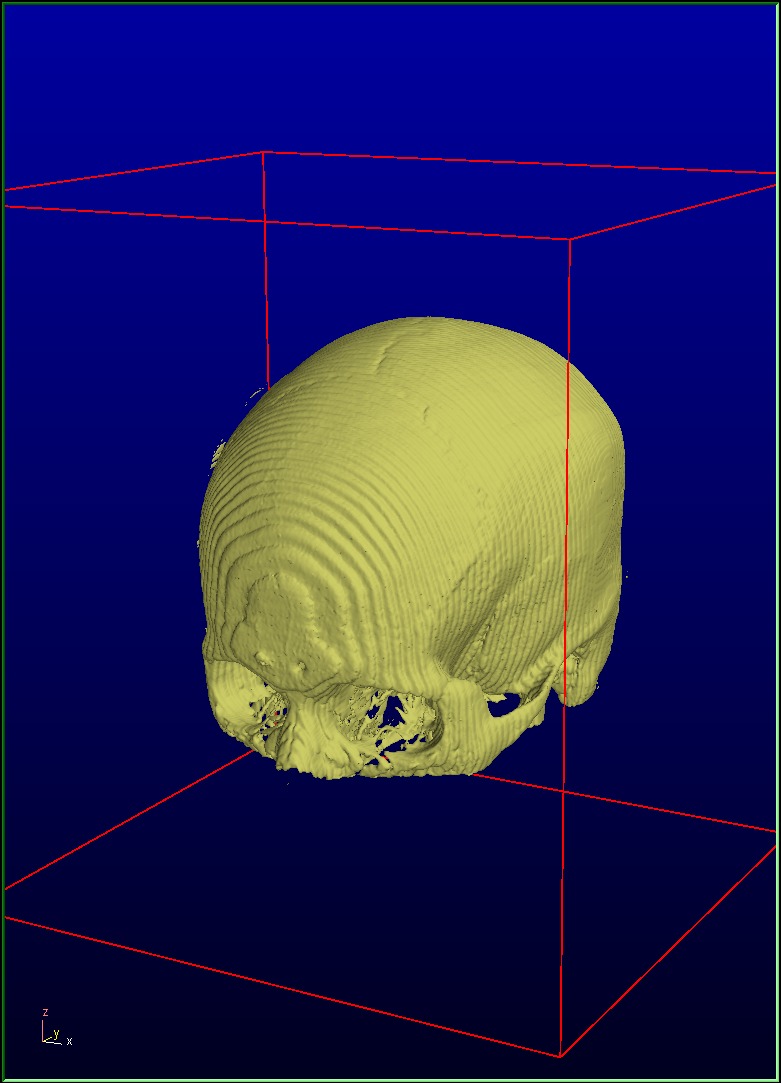
Reslice all datasets: Mean |
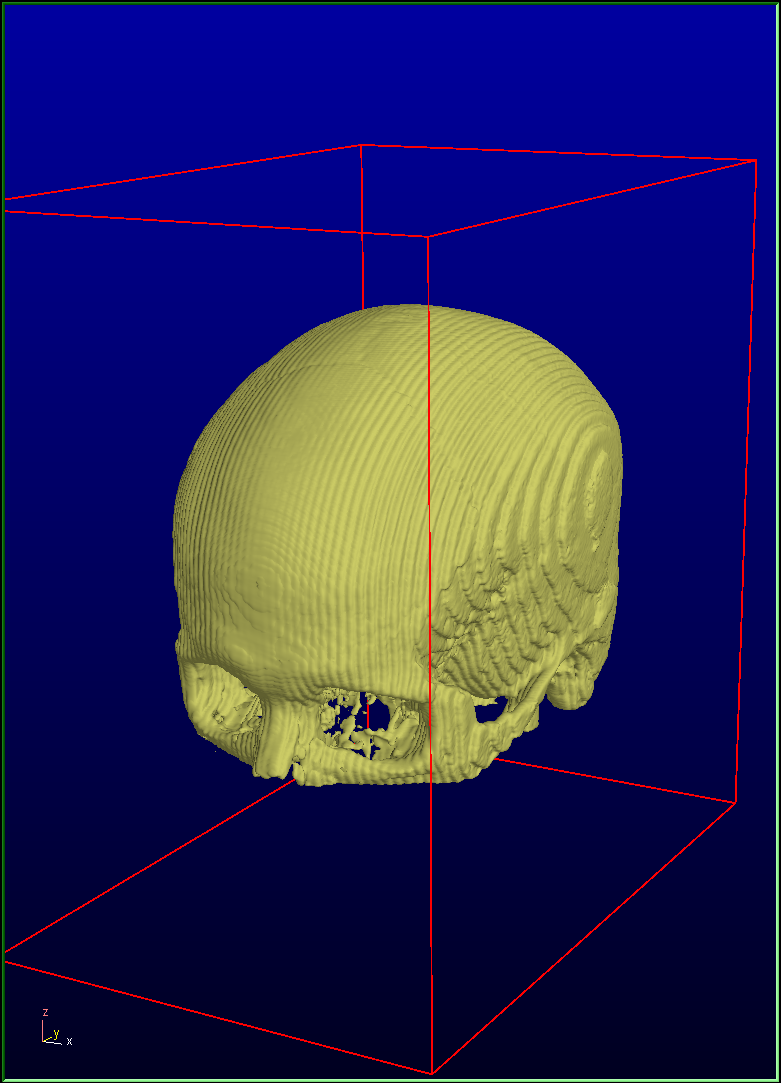
Reslice all datasets: Closest |
Reslice all datasets: Mix |
The new volume will be in the same study as the first of the source groups, but with a series number starting at 100 (if you compute multiple volumes, the series number will be incremented by 1 each time).
If the re-sliced voxels are smaller than the source voxels, they are computed by cubic interpolation from the original voxels at that location. If the re-sliced voxels are larger than the source voxels, it is sub-sampled at the resolution of the source and the mean value of these sub-samples is used.
So, when you click compute, here's what happen:
•For each source groups, we compute the position of each corners of the re-sliced voxels in this source group.
•If you have multiple source groups and selected either the "Max" or "Mix" merge method, we compute the distance between the center of each re-sliced voxels and the closest center of source voxels for each source groups.
•We compute the new voxel values (GLI and TAG) for each of the re-sliced voxels, using the previously computed corner positions, using either interpolation or sub-sampling as needed.
•A new group of re-sliced data is created.
From the Graphic Interface
The Oblique direction window
|
|
|
Oblique angles |
The oblique slice direction is defined by 3 successive rotations: Alpha (α) a first rotation around "X", Beta (β) a second rotation around "Y" and Gamma (γ), a third rotation around "Z". The values of these 3 angles are displayed at the top of the window. They can also be modified here.
|
Image Preview |
A preview of the volume to re-slice and the new reslice frames can be seen here.
|
α & β sliders |
The sliders on the left and right of the preview window can be used to change the Alpha angle. The sliders at the top and bottom of the preview window change the Beta angle.
|
Slice selection |
The slider under the preview window can be used to scroll through the new "resliced" slices.
|
Angles from 3 points |
|
Done |
Close the Oblique window. |
From the Display Area
There is no Display Area interaction specific to this mode.
From the Keyboard
There is no keyboard interface specific to this mode.
From the Command Line
Resize: dir (axial|coronal|sagittal)
Set the reslice direction.
Resize: resolution (x|y|z) value
Set the reslice resolution.
Resize: size (x|y|z) value
Set the reslice pixel size.
Resize: isotropic (on|off|toggle)
Set the reslice voxels isotropic property.
Resize: alpha value
Set the reslice oblique "alpha" angle.
Resize: beta value
Set the reslice oblique "beta" angle.
Resize: gamma value
Set the reslice oblique "gamma" angle.
Resize: merge (max|mean|closest|mix)
Set the reslice mix mode when there is a group overlap.
Resize: compute
Start the reslice computation.